Common Event Format (CEF)
Each vendor has its own format for reporting event information, these event formats often lack the key information necessary to integrate the events from their devices. The ArcSight standard attempts to improve the interoperability of infrastructure devices by aligning the logging output from various technology vendors. The Common Event Format (CEF) is an open log management standard that improves the interoperability of security-related information from different security and network devices and applications. To simplify integration, the syslog message format is used as a transport mechanism. This applies a common prefix to each message, containing the date and hostname, as shown below.
Mar 16 16:35:23 host message
If an event producer is unable to write syslog messages, it is still possible to write the events to a file. To do so:
- Omit the syslog header (show above);
- Begin the message with the format show below
CEF:Version|Device Vendor|Device Product|Device Version|Signature ID|Name|Severity|Extension
After the mandatory CEF: prefix, the remainder of the message is formatted using a common prefix composed of fields delimited by a bar (“|”) character. The Extension part of the message is a placeholder for additional fields.
Definitions of prefix fields
Version is an integer and identifies the version of the CEF format. Event consumers use this information to determine what the following fields represent.
Device Vendor, Device Product and Device Version are strings that uniquely identify the type of sending device. No two products may use the same device-vendor and device-product pair. There is no central authority managing these pairs. Event producers have to ensure that they assign unique name pairs.
Signature ID is a unique identifier per event-type. This can be a string or an integer. Signature ID identifies the type of event reported. In the intrusion detection system (IDS) world, each signature or rule that detects certain activity has a unique signature ID assigned. This is a requirement for other types of devices as well, and helps correlation engines deal with the events.
Name is a string representing a human-readable and understandable description of the event. The event name should not contain information that is specifically mentioned in other fields. For example: “Port scan from 10.0.0.1 targeting 20.1.1.1” is not a good event name. It should be: “Port scan”. The other information is redundant and can be picked up from the other fields.
Severity is an integer and reflects the importance of the event. Only numbers from 0 to 10 are allowed, where 10 indicates the most important event.
Extension is a collection of key-value pairs. The keys are part of a predefined set. The standard allows for including additional keys as outlined under “The Extension Dictionary”. An event can contain any number of key- value pairs in any order, separated by spaces (“ “). The following example illustrates a CEF message using Syslog transport:
Mar 16 16:43:10 host CEF:0|security|threatmanager|1.0|100|trojan successfully stopped|10|src=10.0.0.192 dst=12.121.122.82 spt=1232
Character encoding
Because CEF uses the UTF-8 Unicode encoding method, please note the following:
- The entire message has to be UTF-8 encoded.
- If a pipe (|) is used in the prefix, it has to be escaped with a backslash (\). But note that pipes in the extension do not need escaping. For example:
Mar 16 16:26:45 host CEF:0|security|threatmanager|1.0|100|detected a malware \| in message|10|src=10.0.0.192 act=blocked a | dst=12.1.1.1
- If a backslash (\) is used in the prefix or the extension, it has to be escaped with another backslash (\). For example:
Mar 16 16:46:10 host CEF:0|security|threatmanager|1.0|100|detected a malware \\ in packet|10|src=10.0.0.192 act=blocked a \\ dst=1.1.1.1
- If an equal sign (=) is used in the extensions, it has to be escaped with a backslash (\). Equal signs in the prefix need no escaping. For example:
Mar 16 16:46:10 host CEF:0|security|threatmanager|1.0|100|detected a malware \= in packet|10|src=10.0.0.192 act=blocked a \= dst=1.1.1.1
- Multi-line fields can be sent by CEF by encoding the newline character as \n or \r. Note that multiple lines are only allowed in the value part of the extensions. For example:
Mar 16 16:46:10 host CEF:0|security|threatmanager|1.0|100|detected a malware \n in packet|10|src=10.0.0.192 msg=blocked a \n No action needed dst=1.1.1.1
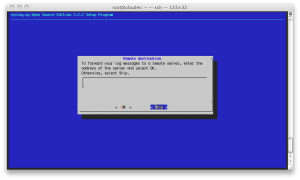
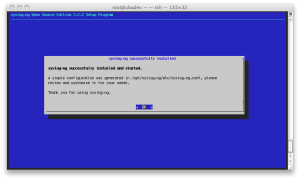
 The last step asks user if he wants forward the log messages to a remote server; we choose “skip”.
The last step asks user if he wants forward the log messages to a remote server; we choose “skip”.